Obesity – Definition – Causes – Treatment

Weight Loss : The BiBble – Read How to do it…!
December 26, 2018
Buy PhenQ : Guide with Frequently Asked Questions & Answers
December 26, 2018Obesity – Definition – Causes – Treatment
1. Overview
Obesity is a term used for an individual who is overweight with a high degree of body fat. The small excess of kilos from a natural weight possibly does not create serious problems, but from the moment you have some kilos more, then it is rather certain that you create symptoms affecting your daily life.
It is a complex disorder, involving a highly excessive amount of body fat. It increases the risk of diseases as heart diseases, diabetes and hypertension.
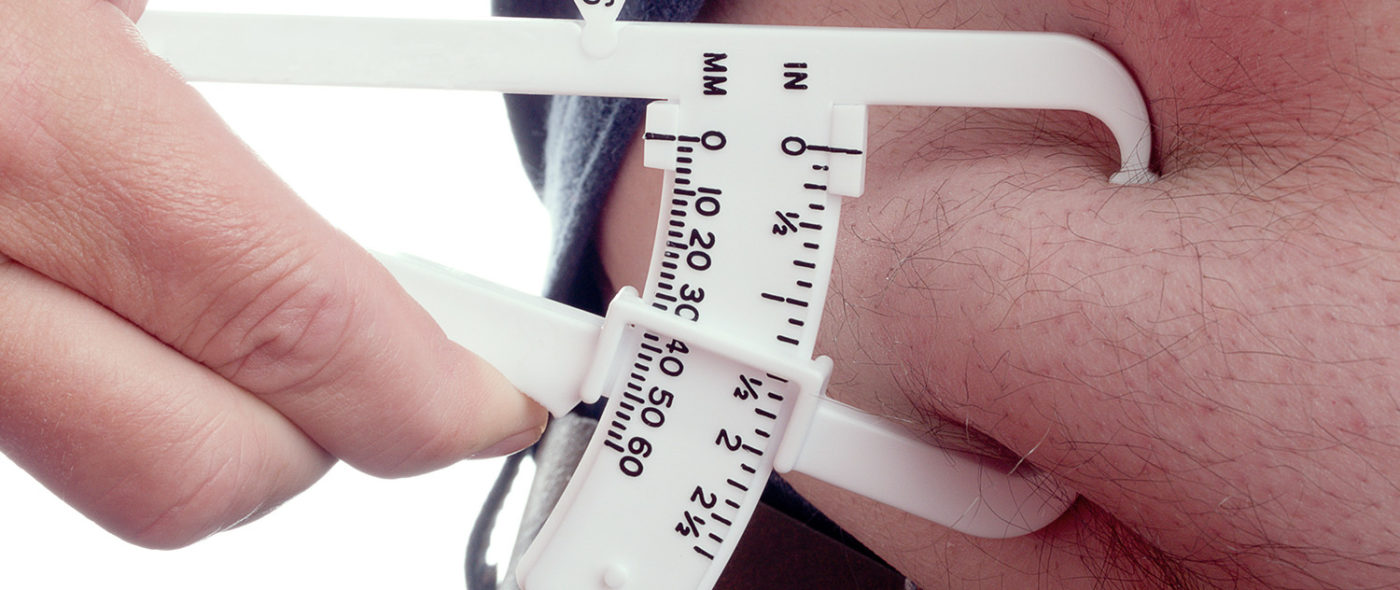
The most popular way of estimating a person’s weight is the Body Mass Index (BMI), which is calculated by dividing your weight in kilos by the square of your height in meters.
If your BMI is:
Between 25 and 29, you’ll be considered as overweight Between 30 and 40, you are obese Over 40, you’ll be considered as very obese
Another method of evaluating the weight is by measuring the waist.
Men with a figure of 94cm. or more and women with a figure of 80cm. or more are potential candidates for presenting health problems related to obesity such as, diabetes type 2, heart problems and certain forms of cancer.
The good news is that even a moderate weight loss may improve or prevent health problems related to weight. Nutritional changes, an increased physical activity, nutritional supplements and changes of the lifestyle may help you to lose weight.
Medicines under prescription and a surgery for weight loss are additional options for the treatment of obesity.
2. What causes obesity
2 .a A general overview
Though a number of influences as genetic, hormonal and of behavioral nature are exercised on the body weight, obesity is observed when you receive more calories than those required for all your daily activities. Your body stores these excess calories as fat.
In certain cases obesity may be related to medical reasons. However, these disorders are very rare and in general the causes for obesity are:
a. No activity. If you are not active, you do not burn enough calories. With a sedentary lifestyle, you can get extra calories on a daily basis than those you eventually use and need in exercise and daily activity.
b. Unhealthy diet and unhealthy eating habits. Weight gain is inevitable if you do not burn enough calories. And it is true that most people’s diet is high in calories, including largely fast food and high-calorie drinks as well.
2.b Risk factors
Usually obesity is the result of a combination of causes and factors contributing on this condition including:
Genetic. Your genes are capable of influencing the amount of fat you store and the exact point where this fat is distributed. Genetics also plays a role in the way your body converts food into energy and the way your body burns calories during exercise.
Family life. Obesity tends to run in families. If one or both of your parents are obese, the risk of you being obese is elevated. This is not because of genetics. Family members tend to share a similar diet and habits of activity.
Inaction. If you are not active / or you will not consume enough calories. Sedentary work or lifestyle predispose you to increase your calorie intake, which is ultimately more than you need during the day. Also, medical problems such as arthritis can lead to decreased activity and thus increase your body weight.
Unhealthy nutritional programme – diet. A diet high in calories and in the absence of fruits and vegetables, including a large percentage of fast and ready meals and soft drinks or high calorie drinks, or even large portions of food contributes to weight gain.
Medical problems. In some people, obesity can be attributed to medical causes, such as syndromes and other conditions. Pathological conditions leading to decreased activity also contribute to weight gain.
A certain number of medicines. Some medications can also lead to weight gain if they are not balanced by similar activities or exercise. These medicines include antidepressants, anti-diabetes medicines, antipsychotic medicines and others.
Social and economic problems. Research has linked social and economic problems to obesity. Preventing obesity is difficult when there are no safe places for your workout. Similarly, you may not be taught healthy cooking habits, or you probably do not have the money needed to buy healthier foods. Additionally, the people you interact with may have some influence on your weight you are likely to become obese if you have friends or relatives obese.
Age. Obesity can occur at any age, even in young children. But as you get older, hormonal changes and reduced activity in your lifestyle increase the risk of obesity. In addition, the muscle volume of your body tends to decrease with age. Smaller muscle volume leads to decreased metabolism. These changes also require fewer calories and can make it more difficult to avoid extra weight. If you consciously do not control what you eat and do not become more active as you grow up, then you increase your weight.
Pregnancy. During pregnancy, each woman’s weight increases necessarily. Some women find it terribly difficult to lose these extra kilos after the child’s birth. This weight gain can lead to obesity in women.
Quitting smoking. Giving up smoking is also associated with weight gain in many cases. And to some people it is possible to touch such figures that make the individual obese. In the long run, however, quitting smoking is a greater benefit to your health than its continuation.
Lack of sleep. Not filling up several hours of sleep, or consuming long sleeping times, can cause changes in your hormones and thus increase your appetite. You may also feel a tendency for foods with a higher number of calories and hydrocarbons, which eventually increase your weight.
If you have one or more of the above risk factors does not necessarily mean you are meant to be an obese person. You can balance most of these risk factors through diet, exercise and activity, nutritional supplements and changes in your lifestyle behavior.
3. Complications
If you are obese, it is highly possible to develop a series of serious health problems which include:
- High triglyceride levels and low levels of high density cholesterol (HDL)
- Type 2 diabetes
- Hypertension
- Metabolic syndrome – combination of high sugar, hypertension, high triglycerides and low cholesterol (HDL)
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Cancer, including uterine, cervical, endometrial, tubal, breast, bowel, colon, esophagus, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, kidney and prostate cancer
- Breathing disorders, including sleep apnea, a really serious disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts
- Disease of the bladder
- Gynecological problems, such as a bloody and irregular period
- Erectile dysfunction and sexual health problems
- Fatty liver disease, a condition in which fat is developed in the liver which can cause inflammation or scarring
- Osteoarthritis
4. Quality of life
When you are obese, the overall quality of your life may be reduced dramatically. You may not be able to do things you usually did, such as engaging in fun activities. You may even avoid public spaces. Obese people may face discrimination.
Other problems that are related to your weight and which are likely to affect your quality of life include:
- Depression
- Impotence
- Sexual problems
- Shame and guilt
- Social isolation
- Achievements of lower quality at work
5. Treatment
The purpose of treating obesity is to reach and stay at a healthy weight. You may have to work with a team of professionals – including a dietician, an obesity specialist – to help you understand and make changes to your diet and your habits of activities.
All weight loss programs require changes in your eating habits and increased physical activity. The methods that are right for your individual case depend on the level of obesity you are in, the overall picture of your health, and your will to participate in a weight loss program.
Other ways of treatment include:
a. Nutritional changes
b. Exercise and activities
c. Change of Behavior
d. Prescription drugs
f. Weight loss surgery
5.a. Nutritional changes
Reducing calories and practicing healthier diet methods are vital to overcome obesity.
Although you may lose weight at the beginning, slow and steady weight loss over a long time is considered as the safest way to lose weight and maintain the desired weight permanently.
Avoid drastic diets and changes because they do not help you maintain the weight you lost over a long time.
There is no better diet. Choose a diet containing healthy foods and it suits you.
Nutritional changes include:
5.a.1 Reduction of calories. The key to the success of any nutritional change is the number of calories you receive. You should, with the help of a specialist or your doctor, calculate the exact number of calories you need to boost your weight loss effort.
5.a.2. Feeling satisfied with smaller food quantities. The principle of energy density can help you satisfy your hunger with fewer calories. All foods have a certain number of calories in a given quantity (volume). Some foods – like sweet and processed foods – are high in energy density.
5.a.3. Choosing healthier choices. To make your diet more hygienic, you consume more plant foods and whole grain hydrocarbons. You also prefer lean protein.
5.a.4. Restricting certain foods. Consult your doctor as some diets limit the amount of a group of foods, such as high-fat and full-fat foods.
5.a.5. Replacing meals. Some diets suggest replacing one or two meals with their products. And in this case see what suits you and how you can keep a desired constant weight with a practical diet
5.b. Exercise and activities
Increased physical activity or exercise is an important part of treating obesity. Most people capable of maintaining their weight for a longer period of time, follow a regular form of exercise, even simple walking.
To boost your activity:
5.b.1. Exercise. People who are obese or overweight should dedicate at least 150 minutes of conservative physical exercise per week. Depending on the weight loss you desire, the total length of time may be adjusted.
5.b.2. Continue to move. Although aerobic exercise is considered as the most effective method for weight loss, you make any changes you can in your everyday life to move more and more, both in time and distance.
5.c. Counseling sessions
Every person is different and deals in a different way to overcome the obstacles. Try to implement programs that fit perfectly to you and to your behavior. Only then you achieve your goal completely.
Try to get some advice from your GP or dietician, or from some support groups as we call them, where there are people with similar problems with you. Exchange ideas, analyze your experiences and listen to other people and feel that there is some help that you can always count on.
5.d. Nutritional supplements
In recent years there are many nutritional supplements as we call them, available in the market which can at different stages strengthen and promote your real effort.
Be informed and select the supplement (s) fitting perfectly with you and your purpose. Your choice should be very careful to avoid dangerous and illegal preparations which in the end can cause serious problems to your health and body.
5.e. Surgery for weight loss
In certain case the surgery for weight loss, the so called bariatric operation, is another option. The weight loss surgery limits the amount of food you can eat comfortably, or reduces the absorption of food and calories or both. While surgery offers the best chance of losing weight, it can expose you to serious dangers.
Surgery is considered as an option if you have tried other methods that have failed and:
– If you have a high degree of obesity (BMI 40 or higher) – BMI is between 35 and 39.9 and you also have a serious health problem related to your weight, such as diabetes or hypertension – You are determined to make all the changes required to make the operation work.
There is no guarantee that you will lose all of your extra weight, or maintain the desired weight for a long time. The success of surgery depends on your will to make changes to your lifestyle and your eating habits for the rest of your life.
Common weight loss procedures include:
5.e.1. Gastric bypass surgery. In this surgery, the surgeon creates a small bag in the upper part of your stomach. The small intestine is then cut shortly below the main stomach and attached to the new bag. Foods and liquids flow directly from the bag into this part of the bowel, bypassing most of your stomach.
5.e.2. Laparoscopic adjustable tape (LAGB). With this procedure your stomach is divided into two bags with an inflated film. Tightening the tape, like a belt, the surgeon creates a small channel between the two bags. The tape keeps the opening from expansion to a fixed diameter and is designed for permanent application.
5.e.3. Cholegarage deflection with a duodenal switch. This procedure starts with the surgeon removing most of the stomach. Leaves the valve releasing the food in the small intestine and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). Then closes the middle part of the intestine and adapts the last part directly to the duodenum. The separated portion of the intestine is re-adjusted to the end of the intestine to allow bile and digestive fluids to flow into that part of the intestine.
5.e.4. Gastric sleeve. With this procedure part of the stomach is removed, creating a smaller space for food. It is a more simplified procedure than the gastric bypass or diversion mentioned above.
6. Preventing the return of weight following the treatment of obesity
It is a common phenomenon to regain weight after a specific treatment of obesity followed. There is no other way to avoid it but by maintaining a regular physical exercise program.
Set as target about 60 minutes a day.
Keep track of your physical exercise and the change, if any, of your weight.
Only by keeping a full body diary you will be able to stay at the desired weight.